Hello There,
Below is from the internet what I finished learning about API vs Web Service.
Please note that my focus is on ASP.NET Web API.
Tomorrow, I will learn more English.
This coming weekend or next Monday, I will start to play with ASP.NET Web API CRUD (ASP.NET MVC and C#), Angular to consume this ASP.NET Web API CRUD, then ASP.NET MVC and C# to consume this ASP.NET Web API CRUD, and then finally jQuery to consume this ASP.NET Web API CRUD.
Regards,
Jimmy Lam
18 August 2022
API (Application Programming Interface) is used as an interface between two different applications for communicating with each other.
Web service is used to communicate between two machines on a network.
The crucial distinction between a web service and an API is that we can use APIs offline and locally, while we must use a web service online. Because you can use APIs on the same machine instead of strictly over a network connection, some APIs do not require a network to be able to interact with them.
Yes, there’s overlap between the two: all web services are APIs, but not all APIs are web services.
Essentially, an API allows two software programs to communicate with each other. One program can call another program’s API to get access to data or functionality of the other program.
API Example 1:
To understand exactly how an API works, consider this non-technical example. When you go to a restaurant, a waiter will take your order and report it to the kitchen. The kitchen makes your food, and the waiter brings it back to your table.
In this example, one program is you (the person ordering food), and one program is the kitchen. The waiter represents the API, that is used to receive requests and return something. In this case, the waiter returns your order, but an actual API would return data or other functionality.
API Example 2:
But data transfer is just one part of what APIs do. APIs also allow you to expose the functionality of applications across the web. Think of it like this. You have a date night with your girlfriend and she says she wants to stay indoors and eat Mexican food. Now, you could choose to go to the internet, download recipes for Mexican food, pick one and then start going through all the stress of preparing it yourself. Or you could just order from a restaurant (I know which one I would pick). In this case, the restaurant is the API, exposing you to the functionality of Mexican food as a service and you are the consumer of the service.
API Example 3:
You go to the movie site, you enter your movie, name, and credit card information, and behold, you print out tickets.
They are collaborating with other applications. This integration is called “seamless” as you never have a clue when a software role is passed from one application to another.
API Example 4:
Now that we have a basic understanding of APIs, it should be easier to see why APIs are so essential in programming. For a slightly more technical example, consider how APIs might play out using a ride-share app as an example. First, you sign up for the ride-share application. Then, you can map your route, find your driver, and pay for the ride all without ever leaving the app.
The ride-sharing app is likely using APIs to make all of this work. For example, an API like Telesign could verify that you own the phone number you provided at sign up. Calculating the time and distance of the ride is probably done with a maps API. An SMS API like Nexmo could notify you that the driver has arrived at the pickup location. When it’s time to pay, your payment is likely processed with an API like Stripe. Finally, when you get a receipt for your ride, an API like SendGrid sends it to your email.
This is one example of how APIs can be used together to quickly add functionality to an application.
Here, are some reason for using API:
Here are some important features of API:
A Web API is a API. A Web API is an application programming interface which is use either for web server or a web browser.
Two types of Web APIs are 1) Server-side API 2) Client-side API
(a) Server-side:
Server-side web API is a programmatic interface that consist of one or more publicly exposed endpoints to a defined request–response message system. It is typically expressed in JSON or XML
(b) Client-side:
A client-side web API is a programmatic interface helps to extend functionality within a web browser or other HTTP client.
Let's stop API here and look into Web Service below:
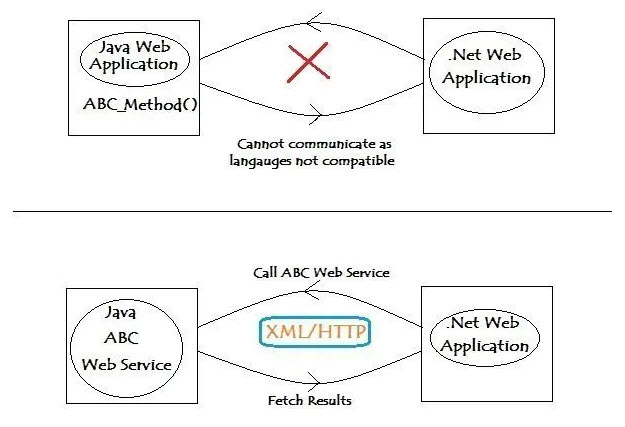
A Web service is a web application that can communicate with other web-based applications over a network. Web services implementation allows two web applications developed in different languages to interact with each other using a standardized medium like XML, SOAP, HTTP etc.

Now web services are very similar to APIs, with one major difference: they require a network to communicate. Therefore, we can define web services as a resource that allows machine-to-machine communication over a network using a few set protocols and standardized commands. Most web services are built using SOAP protocols, but they can also be built using REST and XML-RPC (remote procedure call) protocols and they only communicate via HTTP protocols (they do not support HTTPS). Also, most web services are designed to offer a specific type of data or functionality to a specific partner. Think of them as a designated driver for a public figure. His job is to drive and he can probably drive any type of car with any type of person in it, but he’s restricted to driving just that one person.
Modern day business applications use variety of programming platforms to develop web-based applications. Some applications may be developed in Java, others in .Net, while some other in Angular JS, Node.js, etc.
Most often than not, these heterogeneous applications need some sort of communication to happen between them. Since they are built using different development languages, it becomes really difficult to ensure accurate communication between applications.
Here is where web services come in. Web services provide a common platform that allows multiple applications built on various programming languages to have the ability to communicate with each other.